论文学习:Who is Real Bob? Adversarial Attacks on Speaker Recognition Systems
文章题目:Who is Real Bob? Adversarial Attacks on Speaker Recognition Systems
来源:2021 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP)
Introduction
Motivation
- the impacts of adversarial attack in the practical black-box setting are still open
Challenge
- C1:Crafting adversarial samples as less imperceptible as possible in the black-box setting.
- C2:Making the attack practical, namely, adversarial samples are effective on an unknown SRS, even when playing over the air in the physical world.
Contribution
- To our knowledge, this is the first study of targeted adversarial attacks on SRSs in the black-box setting. Our attack is launched by not only using gradient estimation based methods, but also incorporating the score threshold into the adversarial sample generation. The proposed algorithm to estimate the score threshold is unique in SRSs
- Our black-box attack addresses not only the speaker recognition tasks considered by existing white-box attacks but also the more general task, open-set identification, which has not been considered by previous adversarial attacks.
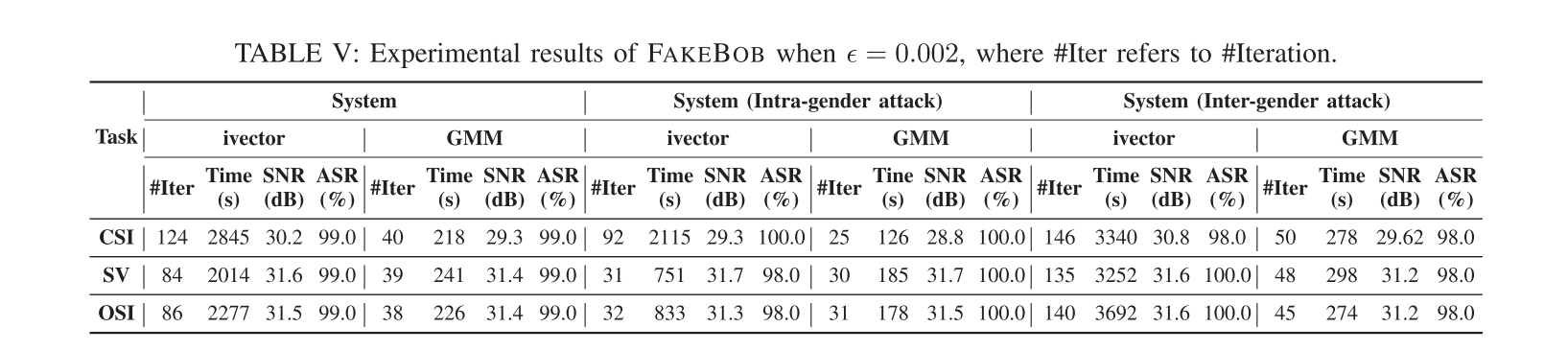
- Our attack is demonstrated to be effective on the popular open-source systems and commercial system Talentedsoft, transferable and practical on the popular open-source systems and the open-set identification task of Microsoft Azure even when playing over the air in the physical world.
- Our attack is robust against four potential defense methods which are reported very promising in speech recognition domain. Our study reveals the security implications of the adversarial attack on SRSs, which calls for more robust SRSs and more effective domain-specific defense methods.
Threat Model
Attack scenarios
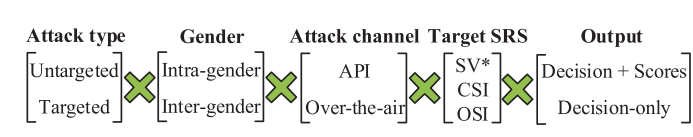
Attack hypothesis
- adversary has some voices of the target speakers to build a surrogate model, while these voices are not necessary the enrollment voices。即对于targeted attack,假设adversary能够拥有desired target speaker的voice,从而能够query black-box SRS得到对应的score和decision
System design
FAKEBOB overview
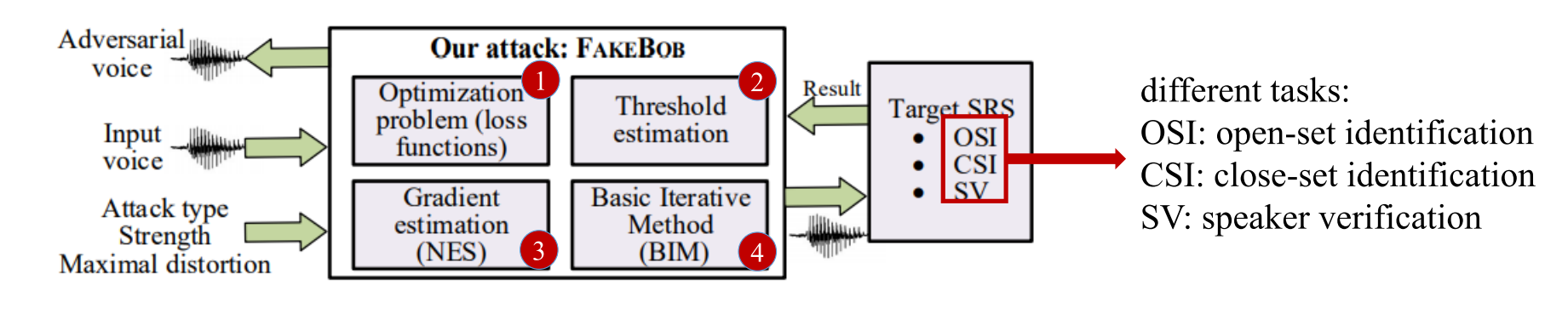
为了生成adversarial example,也是将其定义为一个最优化问题(optimization problem),即最小化一个自定义的loss
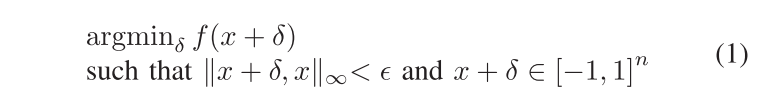
$f\left( \right)$即为loss function,$x$是source voice。所有input先会经过normalization到[-1,1],然后加上扰动(perturbation)$\delta$,得到adversarial example,最后经过一个逆变换过程将数据恢复到原始scale。
该loss会根据不同的targets SRS,略作修改,总体思想是使得source voice加上扰动(perturbation)$\delta$后(即成为adversarial voice)与victim voice越来越像,并且设置一个参数$\epsilon$来限制$\delta$的强弱。
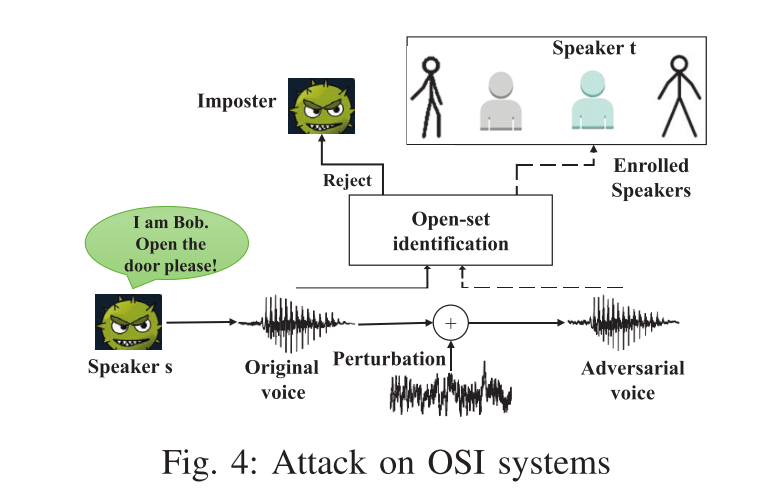
Attack on OSI
OSI作为本文主要攻击目标,因为它目前商用SRS最为重要的应用场景
targeted attack loss:
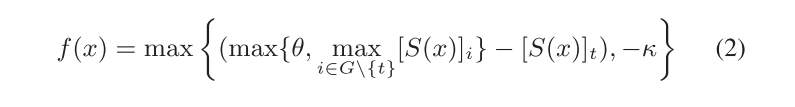
untargeted attack loss:
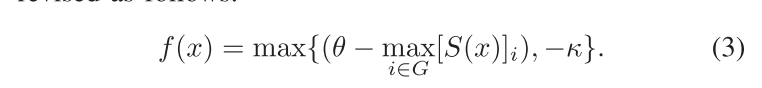
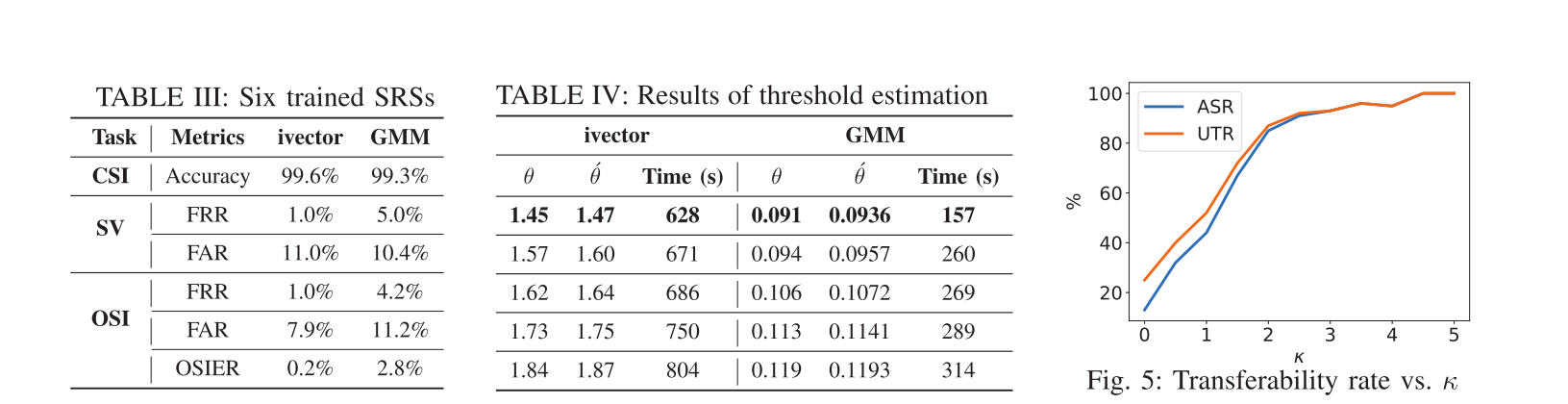
该文主要攻击target是OSI SRS,且是black-box setting,所以无法得知SRS具体的threshold,因此本文提出了一种threshold estimation算法,如下图:
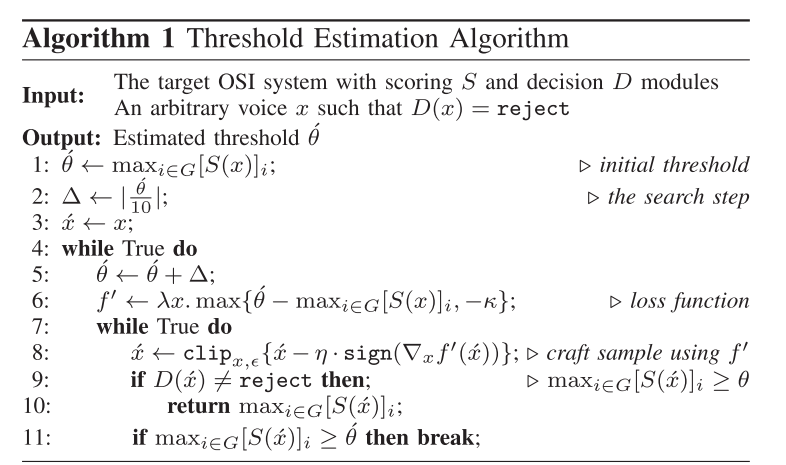
该算法使得estiamted threshold not less than real threshold(not seen to adversary)
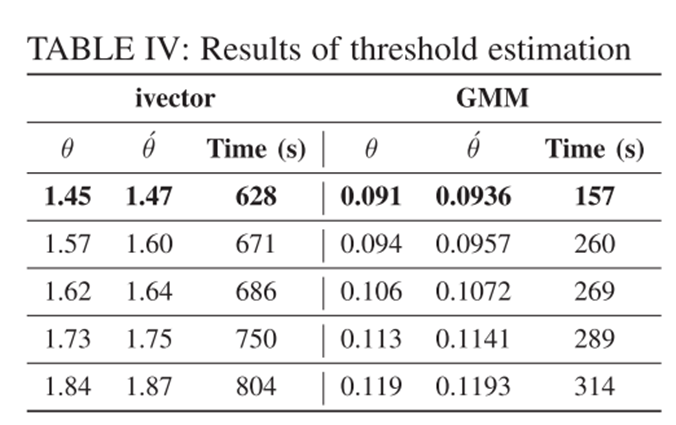
文章也通过实验评估了该threshold estimation算法的有效性
同样地,由于是black-box setting无法得知SRS具体的loss function和内部parameters weights,也就无法使用gradient-based mehtod(直接)来生成adversarial example。为了解决这一问题,使用NES算法(Natural Evolution Strategy)来得到estiamted gradient,然后使用BIM(Basic Iterative Method)进行estimated gradient descent来得到最优的adversarial example。
BIM公式如下:
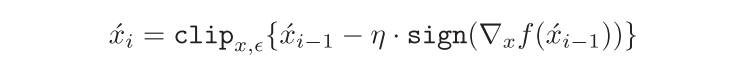
其中$\acute{x}_0=x$,clip函数是为了对扰动$\delta$加以限制,具体为:
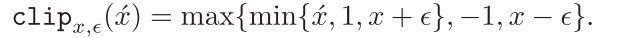
NES生成estimated gradient公式如下:
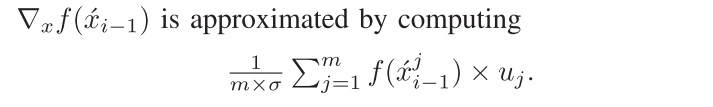
$u_j$是每轮iteration随机生成的Gaussian noises,是一个向量$\left( u_1,…,u_m \right)$,服从高斯分布。然后将这个向量的每个元素分别加到$\acute{x}_{i-1}$得到$\acute{x}_{i-1}^{1},…,\acute{x}_{i-1}^{\boldsymbol{m}}\ \boldsymbol{where\ }\acute{x}_{i-1}^{j}=\acute{x}_{i-1}+\sigma \times u_j
$
而且$u_j=-u_{\boldsymbol{m}+1-\boldsymbol{j}}\ \boldsymbol{for\ j}=1,…\frac{\boldsymbol{m}}{2}$
其中$m=50$,$\sigma =1e−3$,均为超参数,本文已经设为定值
Attack on CSI
CSI没有threshold设定,因此loss相对简单,具体如下:
targeted attack loss:
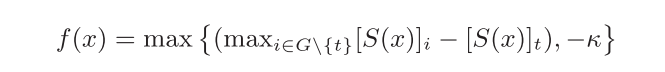
untargeted attack loss:
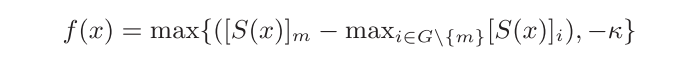
Attack on SV
由于SV是一个一对一问题,因此targeted attack和untargeted attack的目标是一样的,具体Loss:
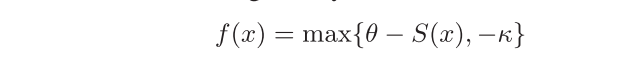
由于只有一个enrolled speaker,因此在生成estimated threshold时候,需要换成:
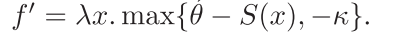
Evaluation
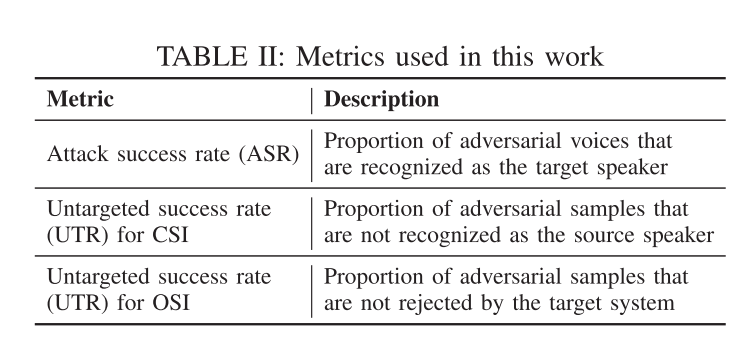
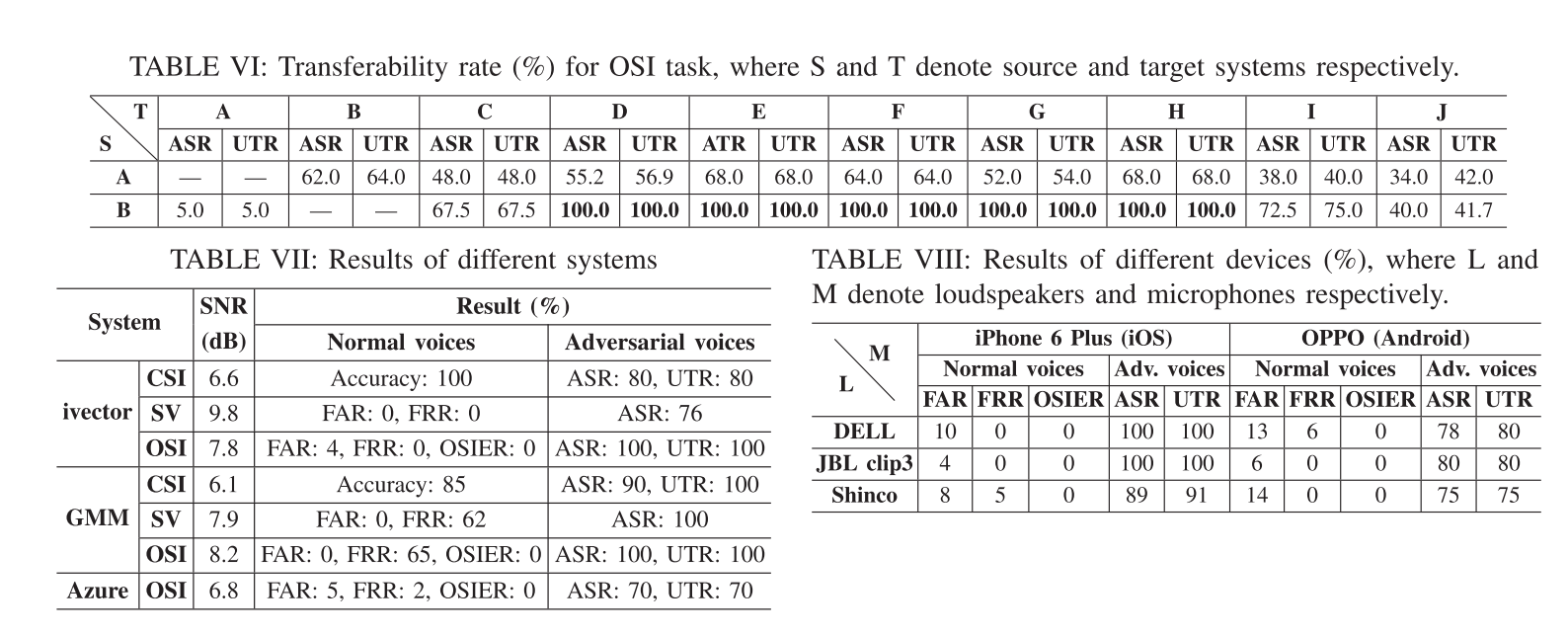
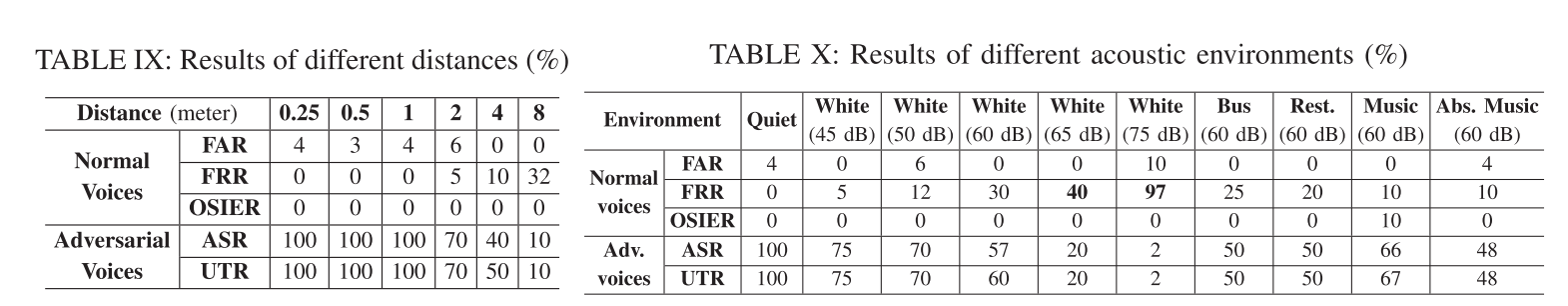
本文做了大量详尽的evaluation,详见原文appendix
问题
- 实现practical attack仅仅是加强了perturbation strength,而不是建立noise model,原文给出的原因是害怕产生environment and device-dependent。这会导致攻击的不可感知性(imperceptibility)大幅下降,特别是进行over-the-air attack时
- room simulators to approximate the actual RIR
- RIR augmentation techniques:direction-to-reverberant ratio (DRR)
- 文中提出的方法只适用于score和decision都能得到的black-box SRS,如果只能得到decision,原文中只能使用transfer attack
- 无法抵抗liveness detection,即无法做到实时生成adversarial example(无法在live user说话时,实时生成相应的perturbation)
- 因为定义的loss optimization problem很难解,使得迭代生成adversarial example时间较长(基本都在10min以上),感觉实际应用场景很少